Light of the Silver Rose. Found in plants and some microorganisms eg.

Leaf Wikipedia

Leaf Structure Cie Igcse Biology Revision Notes

Biology Photosynthesis
The energy excites one of its electrons enough to leave the molecule and be transferred to a nearby primary electron acceptor.

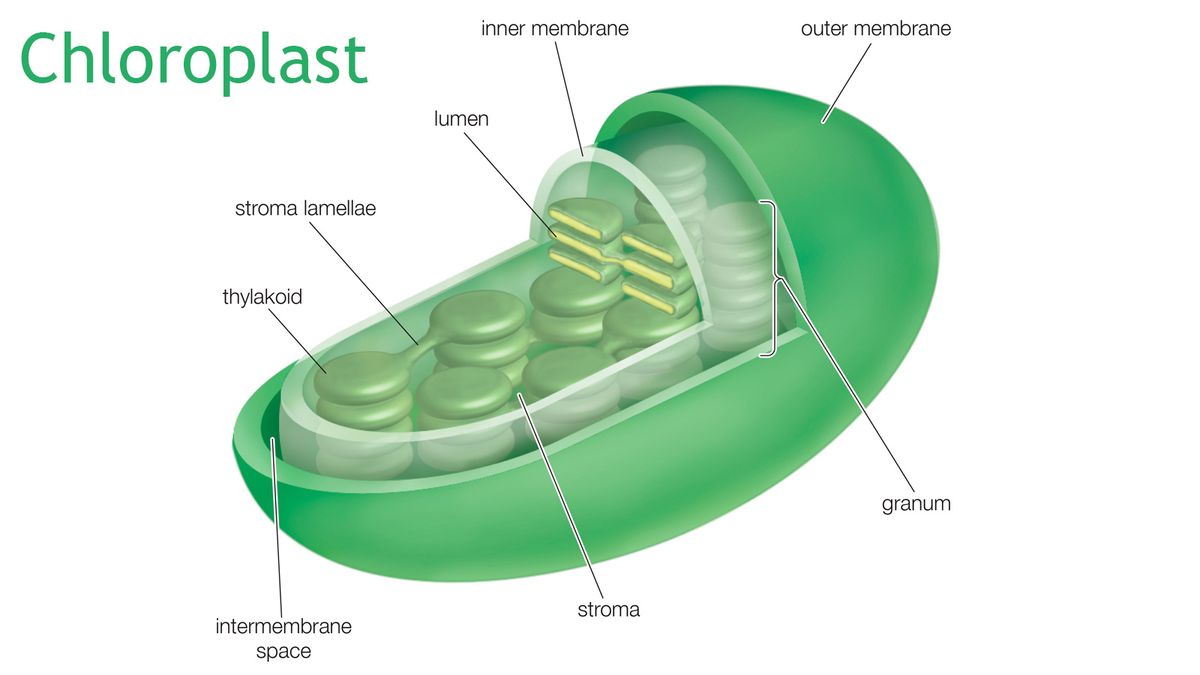
Leaf inner structure and light absorbed. It is present on both sides of the leaf and is called the upper and lower epidermis respectively. Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that through cellular respiration can later be released to fuel the organisms activitiesThis chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules such as sugars and starches which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water hence the name photosynthesis from the Greek phōs. Within the chloroplast is a third membrane that forms stacked disc-shaped structures called thylakoids.
It builds up oxygen from the light reactions in the leaf. Some organisms grow underwater where light intensity decreases with depth and certain wavelengths are absorbed by the water. The epidermis helps in the regulation of gas exchange.
The specific chloroplast structure that contains the photosynthetic pigments is the - outer membrane - stroma - inner membrane. Botanists call the upper side the adaxial surface or adaxis and the lower side the abaxial surface or abaxis. Plant Cell Diagram 1 Cell Wall.
An antenna complex consisting of a large set of pigment molecules that capture light energy and feed it to the reaction center. Take a well-watered healthy potted plant and cover the pot with the help of rubber sheet. Once that light energy is absorbed the carotenoids pass that energy on to a neighboring chlorophyll molecule.
The size of the stomatal openings is variable and regulated by a pair of guard cells which respond to the turgor pressure water content of the leaf thus when the leaf is hydrated the stomata can open. Chloroplast structure within the cells of plants and green algae that is the site of photosynthesis. A young blonde haired man with whisker cheeks of nineteen years and has purple concentric circles covering the eyeballs wearing a black leather trench coat suit with black pants and a top plus boots is seen driving his military like vehicle on a desert region with its wheels floating when he stopped at a site where there are corpses all around.
Where is solar energy absorbed during photosynthesis. Granum is found in the chloroplast of plant cells where photosynthesis occurs. A photosystem consists of two closely linked components.
All of the listed responses are correct. Experiment to demonstrate the transpiration phenomenon with the bell jar method. The light-dependent reactions and the Calvin cycle.
- It is exogenous in origin. The energy culminates in a molecule of chlorophyll found in the reaction center. The leaf is supported away from the stem by a stem-like appendage called a petiole.
The light dependent reaction happens when solar energy is captured to make a molecule called ATP adenosine triphosphate. - The green colour of the leaf is due to the presence of chlorophyll pigment. The first process is the Light Dependent Process Light Reactions requires the direct energy of light to make energy carrier molecules that are used in the second process.
A dorsi-ventrally compressed lateral appendage of stem produced at the nodes and is specialized to perform photosynthesis draarif Morphology of Leaf CHARACTERISTICS OF LEAF. The entire spectrum of white light the infrared the range absorbed by carotenoids. However this concept has not been verified in natural forests especially at a large scale.
In plants chloroplasts occur in all green tissues. Look at the slide with your microscopes 10x objective to see the general structure and higher power to see cell. A machine called a spectrophotometer which is much more sensitive to color than the human eye passes a beam of UV light through a solution and shows how much of the radiation is absorbed by the compound using color changes.
Chlorophyll Definition Structure Function and Photosynthesis Definition. - outer membrane - inner membrane - thylakoid - stroma. Chlorophyll Chl is an important photosynthetic pigment to the plant largely determining photosynthetic capacity and hence plant growth.
Plants on the rainforest floor must be able to absorb any bit of light that comes through because the taller trees block most of the sunlight Figure 511. Chloroplast inner membrane stomata cristae. The effect has found use in electronic devices.
Leaves have evolved to expose the largest possible area of green tissue to light and entry of CO 2 to the leaf is controlled by small holes in the lower epidermis called stomata Figure 2 B. The phenomenon is studied in condensed matter physics and solid state and quantum chemistry to draw inferences about the properties of atoms molecules and solids. Chlorophyll is perhaps the most important naturally occurring pigment on the planet.
It is the outermost protective layer of a plant cell having a thickness of 20-80 nm. - light reactions - Calvin cycle reactions _ synthesize carbohydrates _ release oxygen. Light energy is absorbed by a chlorophyll molecule and is passed along a pathway to other chlorophyll molecules.
In the leaf chlorophyll molecules and carotenoids are situated near each other in clusters somewhat analogous to a dish antenna see Figure 4. The below mentioned article includes a collection of thirteen experiments on transpiration. Leaf Structure and Function.
Cell walls are made up of carbohydrates such as cellulose hemicellulose and pectin and a complex organic polymer called lignin. The blade of a leaf is the. Chloroplasts have a double inner and outer membrane.
The Light Independent Process or Dark Reactions occurs when the products of the Light Reaction are used to. The Light-Dependent Reactions Photosynthesis takes place in two stages. - Leaf is a thin expanded green structure.
Inner barkThe interior. Chloroplasts are a type of plastid that are distinguished by their green color the result of specialized chlorophyll pigments. Other organisms grow in competition for light.
Furthermore how Chl varies in natural forests remains unclear. The chlorophyll in the chloroplasts inside leaf cells absorbs sunlight. Light dependent reactions and light independent or dark reactions.
Explore the world of grana and learn the definition function and importance of these coin-shaped stacks. Parts of a Leaf. The photoelectric effect is the emission of electrons when electromagnetic radiation such as light hits a materialElectrons emitted in this manner are called photoelectrons.
Make a wet mount on a plain slide with the inner part of the leaf section facing up so the inner cells are visible. The outermost layer of the leaf is the epidermis. Scientists use UV light to analyze the chemical structure of a compound via color changes.
And a photochemical reaction center consisting of a complex of proteins and chlorophyll molecules that enable light energy to be converted into chemical energy Figure 14-43. Each leaf develops as a flattened surface that provides a large area for efficient absorption of light energy. You can do this by adding a drop or two of water over the leaf section and then covering it with the coverslip.
Embedded in the thylakoid membrane are molecules of chlorophyll a pigment a molecule that absorbs light through which the entire process of photosynthesis begins. The base of the petiole is attached to the stem at the node. In this study the leaves of 823 plant species were collected from nine typical forest communities.
In the light-dependent reactions which take place at the thylakoid membrane chlorophyll absorbs energy from sunlight and then converts it into chemical energy with the use of waterThe light-dependent reactions release oxygen as a byproduct as water is broken apart. Bell jar well-watered potted plant rubber sheet glass plate Vaseline. The process of photosynthesis is divided into two main parts.
Cyanobacteria these porphyrins play an important role in the conversion of solar energy to chemical energy through a process known as photosynthesis.

Photosynthesis

Why Are Plants Green To Reduce The Noise In Photosynthesis Quanta Magazine

3 Dorsiventral Cross Section Of A Dicot Leaf With The Adaxial Surface Download Scientific Diagram
Nutrition In Plants Upper Sec Science

Internal Structure Of A Leaf

Why Are Plants Green

Leaf Structure Cie Igcse Biology Revision Notes
Chloroplasts Are The Plant Cells That Manufacture Energy Howstuffworks